Blog
It’s obviously one of the most-asked for features of our optical 3D measurement systems – but do you really know what accuracy is? Let’s have a look!
Accuracy is one of the most important features in metrology, referring to the data’s correctness. An accurate measurement system provides measurements that are close to the actual value or standard. Furthermore, accuracy is one of the necessary characteristics to assess a measurement system’s suitability for a particular application. Thus, it is one of the main features of the Bruker Alicona optical 3D measurement systems.
A combination of trueness and precision, accuracy can be derived from the systematic and random errors of a measurement system – both values must be as low as necessary. Quantitatively, systematic errors are indicated as bias value, whereas qualitatively, they are given as trueness. In contrast, random errors are indicated as precision which is often expressed as standard deviation.
One example for highly accurate optical 3D metrology is the µCMM from Bruker Alicona. As the first purely optical CMM on the market, it is used to measure parts with extremely tight tolerances in unrivalled high accuracy, enabling the measurement of small surface details on large components and precisely determining the position of these individual measurements in relation to each other.
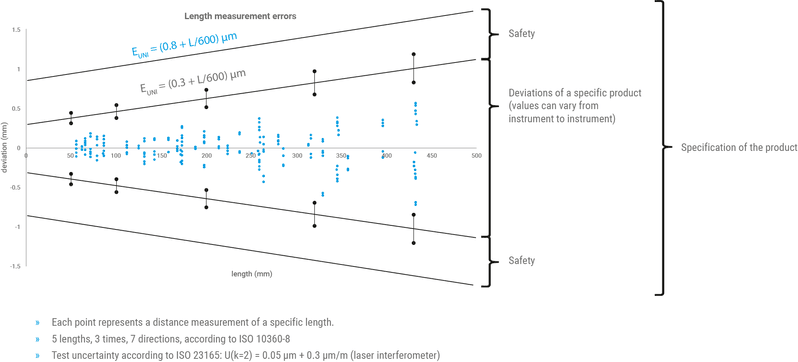
With the µCMM, the length measurement error remains below EUnI = (0.8 +L/600) µm in the entire measurement volume of 310x310x310mm.
The µCMM‘s high level of accuracy even led to a webinar that is dedicated completely to this topic. Watch the free recording.
Want to have a closer look at the µCMM? Click here to learn more.